请注意,本文编写于 1814 天前,最后修改于 63 天前,其中某些信息可能已经过时。
安装开始之前,你需要准备好有游戏本体和对应版本的汉化mod。
特别需要注意的:双子节的版本需要与游戏版本一致,否则会出现闪退等现象
本教程使用的汉化mod版本为:1.29.2
新版本双子节文件可能会比本文截图更多,不过无妨,仍可以使用本文方法进行汉化
同时P社也可能出现单纯“更新”版本行为,这种情况下汉化依旧就能用,双子节需要更新汉化mod

如果是创意工坊订阅的汉化,可以无须准备汉化mod包,直接订阅,然后把双子节安装后即可直接开始游玩
步骤
- 先运行一次英文原版游戏,不需要打开游戏,只需要启动器启动了就可以。然后关闭;

- 打开我的文档中的
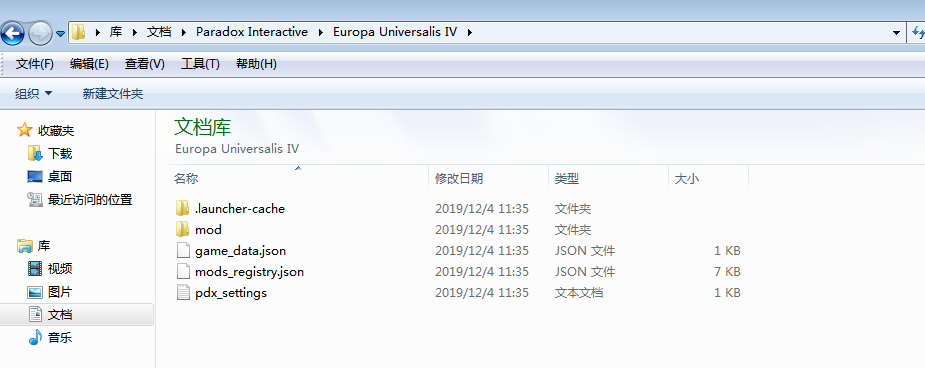
Paradox Interactive\\Europa Universalis IV\\mod文件夹,mod文件夹的上级目录的情况如下图,如果没有mod文件夹就自己创建;
- 解压汉化mod得到四个文件,红色为汉化Mod文件(基础包),蓝色为汉化补丁文件(汉化补充包,增加了人名、动态地名、君主名及舰船名称等汉化,需搭配基础包使用,启用后无法获得成就。)

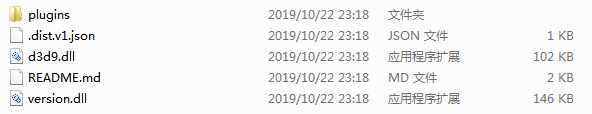
- 把解压后的汉化mod文件放入
我的文档\Paradox Interactive\Europa Universalis IV\mod中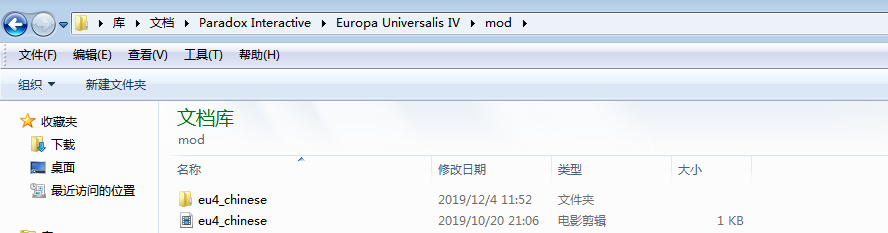
- 解压双子节文件,并把双子节解压后所有文件复制到游戏根目录(根目录即游戏安装目录)下
- 再次启动游戏,点击mod选项卡,启用汉化mod,最后点击开始游戏,就可以开始你的征程了。



总结
如果觉得拖沓,可以直接去看52pcgame上的汉化使用方法,虽然是1.28的,但步骤流程还是一样的。后面追加一下最新工坊的说明和使用



